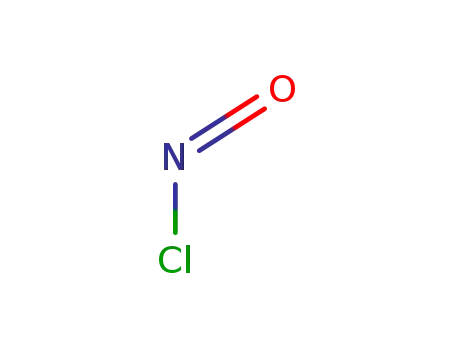
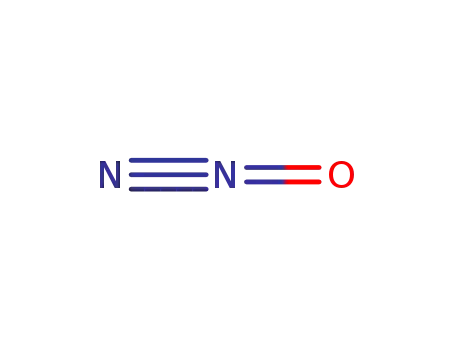
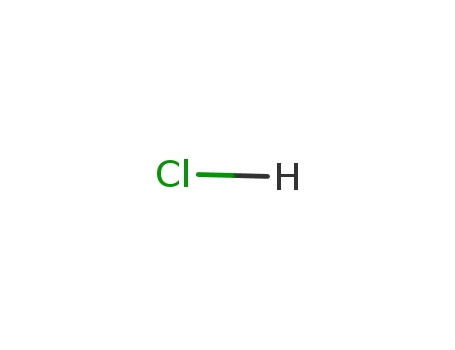
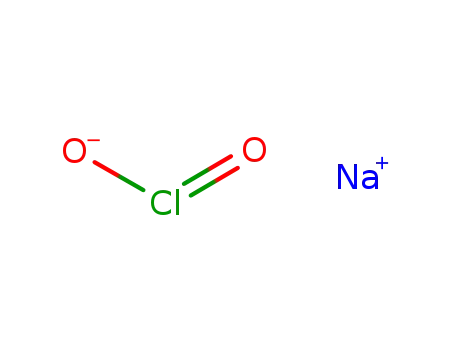
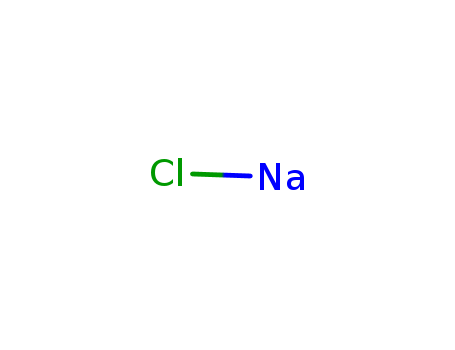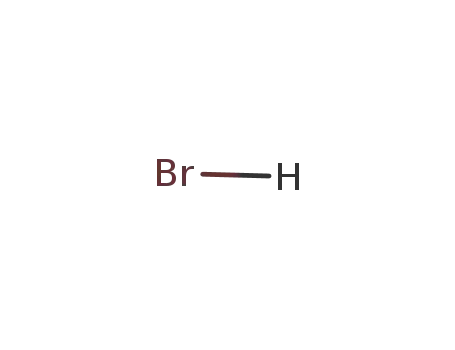Sodium atom Reactions with the Bromochloromethanes: Branching Ratios and Relative Reaction Rates
Jayne, J. T.,Davidovits, P.
, p. 3574 - 3579 (1989)
Branching ratios into bromide and chlori...
Nanosize Effect on the Deliquescence and the Efflorescence of Sodium Chloride Particles
G. Biskos,A. Malinowski,L. M. Russell,P. R. Buseck &S. T. Martin
, Aerosol Science and Technology Volume 40, 2006 - Issue 2
Two independent methods were used to generate the aerosol particles, namely by vaporizing and condensing granular sodium chloride and by electrospraying a high-purity sodium chloride aqueous solution, to investigate possible effects of impurities on the results. The DRH and ERH values were the same within experimental uncertainty for the particles generated by the two methods.
Sodium chloride toxicity and the cellular basis of salt tolerance in halophytes
Timothy J. Flowers, Rana Munns, Timothy D. Colmer
, Annals of Botany, Volume 115, Issue 3, February 2015, Pages 419–431,
The data reviewed here suggest that halophytes tolerate cytoplasmic Na+ and Cl− concentrations of 100–200 mm, but whether these ions ever reach toxic concentrations that inhibit metabolism in the cytoplasm or cause death is unknown. Measurements of ion concentrations in the cytosol of various cell types for contrasting species and growth conditions are needed. Future work should also focus on the properties of the tonoplast that enable ion accumulation and prevent ion leakage, such as the special properties of ion transporters and of the lipids that determine membrane permeability.