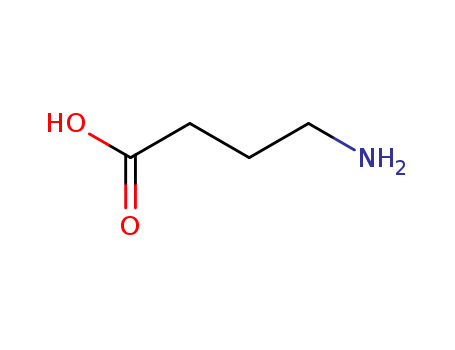
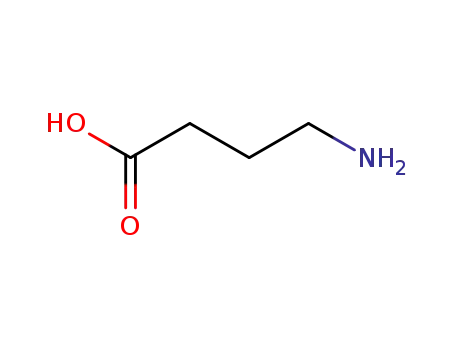
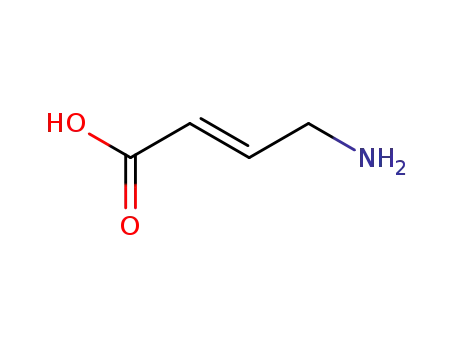
Manufacturer supply 4-Aminobutyric acid 56-12-2 with sufficient stock and high standard
- Molecular Formula:C4H9NO2
- Molecular Weight:103.121
- Appearance/Colour:White microcrystalline powder
- Vapor Pressure:0.00798mmHg at 25°C
- Melting Point:195 °C (dec.)(lit.)
- Refractive Index:1.465
- Boiling Point:247.985 °C at 760 mmHg
- PKA:4.031(at 25℃)
- Flash Point:103.778 °C
- PSA:63.32000
- Density:1.11 g/cm3
- LogP:0.51020
4-Aminobutyric acid(Cas 56-12-2) Usage
| General Description |
4-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS and is formed from L-glutamate via the enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase.
|
|
Uses
|
In vertebrates, 4-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain, regulating ion flow through its receptors (GABAA and GABAB). GABAA receptors are ligand-gated ion channels, while GABAB are G protein-coupled receptors. GABA's excitatory function dominates in developing neurons, influencing chloride gradients that shift as the brain matures. GABAergic mechanisms extend to tissues like the intestine, kidney, pancreas, and reproductive organs. In plants, GABA plays a role in stress responses and ion transport. Research using Lemna plants has shown GABA promoting growth by increasing mineral content. |
| Mechanism of Action |
4-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a critical inhibitory neurotransmitter, primarily regulating CNS activity by binding to GABAA receptors, which control chloride ion channels in neuronal membranes. This action depresses neuronal excitability, leading to effects like sedation, hypnosis, and anxiety reduction when activated by agonists. |
| History |
4-Aminobutyric acid, commonly known as GABA, was first synthesized in 1883. Initially, it was known only as a metabolic product in plants and microbes. However, in 1950, it was discovered to play an essential role in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS), acting as an inhibitory neurotransmitter. |
InChI:InChI=1/C4H9NO2/c5-3-1-2-4(6)7/h1-3,5H2,(H,6,7)
Jilin Tianyun New Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional production enterprise that production, processing, and export, mainly engaged in various organic chemicals. The company has a wealth of professional experience, reliable product quality, reasonable prices, and products are exported to countries around the world, which can meet your diverse needs.
56-12-2 Relevant articles
Receptor modifiers indicate that 4-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a potential modulator of ion transport in plants
Alan M. Kinnersley & Fang Lin
, Plant Growth Regulation, Volume 32, pages 65–76, (2000)
Growth inhibition bybicuculline was not relieved by increasing the amountsof GABA in the medium, indicating that the alkaloid isnot acting, as in the CNS, by competitive antagonismof GABA at GABA receptor sites. Baclofen, a GABAagonist that promotes GABA activity in animalssignificantly increased GABA mediated promotion ofLemna growth. These findings and the knownaction of GABA in regulating ion channels in animalssuggests a way that GABA could amplify the stressresponse in plants.
Determination and correlation of solubility and thermodynamics of mixing of 4-aminobutyric acid in mono-solvents and binary solvent mixtures
Kaifei Zhao , Peng Yang , Shichao Du, Kangli Li , Xiaona Li , Zhenfang Li , Yumin Liu , Lanlan Lin , Baohong Hou , Junbo Gong
, The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics Volume 102, November 2016, Pages 276-286
In this work, by using a laser monitoring dynamic method, the solubility of 4-aminobutyric acid in five mono-solvents of methanol, formamide, 1,2-propanediol, 1,3-propanediol and water, and (methanol + water) binary solvent mixtures was experimentally determined in the temperature ranging from 283.15 K to 323.15 K at atmospheric pressure. The modified Apelblat equation, λh equation and NRTL_Binary model were employed to correlate the solubility of 4-aminobutyric acid in five mono-solvents.
Volumetric and Viscometric Studies of 4-Aminobutyric Acid in Aqueous Solutions of Salbutamol Sulphate at 308.15, 313.15 and 318.15 K
K. Rajagopal a , S.S. Jayabalakrishnan b
, Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering Volume 17, Issue 5, October 2009, Pages 796-804
Density (ρ) and viscosity (η) measurements were carried out for 4-aminobutyric acid in 0.0041, 0.0125 and 0.0207 mol·L−1 aqueous salbutamol sulphate at 308.15, 313.15 and 318.15 K. The measured values of density and viscosity were used to estimate some important parameters such as apparent molar volume Vϕ, limiting apparent molar volume…
56-12-2 Process route
-
-
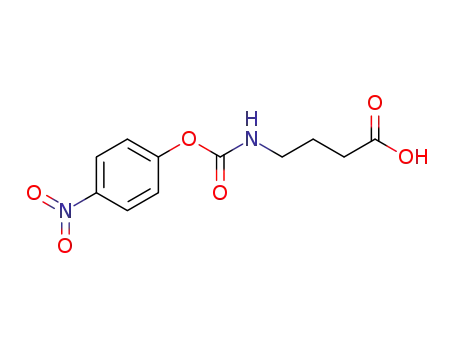
4-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)aminobutanoic acid
-
- 100-02-7,78813-13-5,89830-32-0
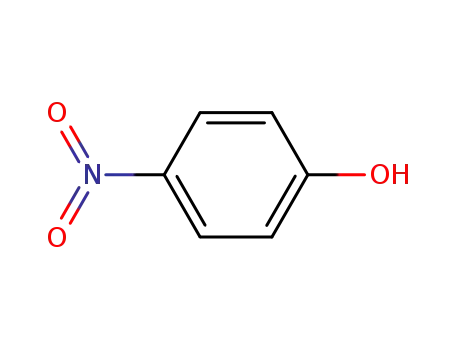
4-nitro-phenol
-
- 56-12-2
4-amino-n-butyric acid
Conditions
| Conditions |
Yield |
|
With water; antibody 33B4F11; at 25 ℃; Rate constant; pH = 7.0, NaCl;
|
|
-
- 284043-11-4
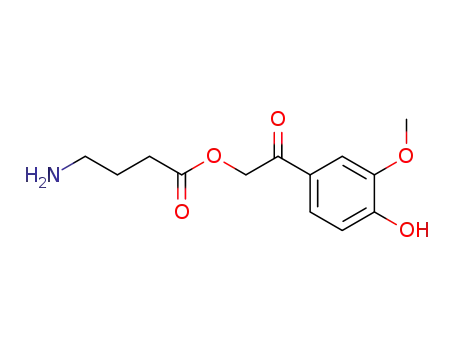
4-amino-butyric acid 2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2-oxo-ethyl ester
-
- 306-08-1
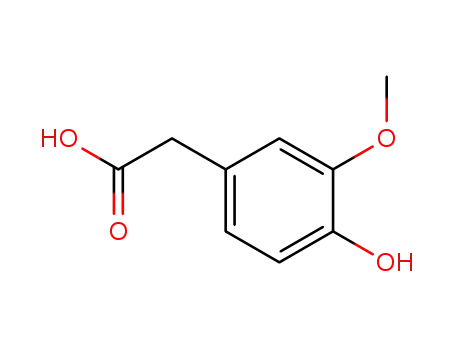
Homovanillic acid
-
- 18256-48-9
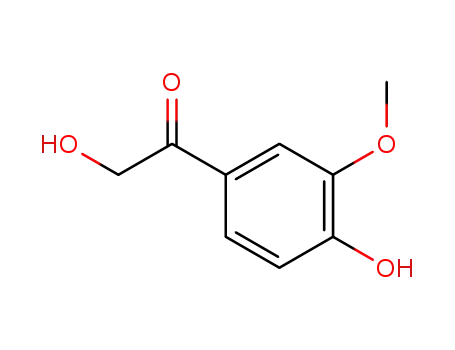
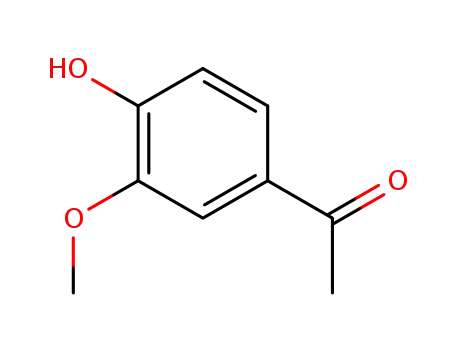
2,4'-dihydroxy-3'-methoxyacetophenone
-
- 498-02-2
1-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone
-
- 56-12-2
4-amino-n-butyric acid
Conditions
| Conditions |
Yield |
|
With water; UV-irradiation;
|
|
56-12-2 Upstream products
56-12-2 Downstream products
-
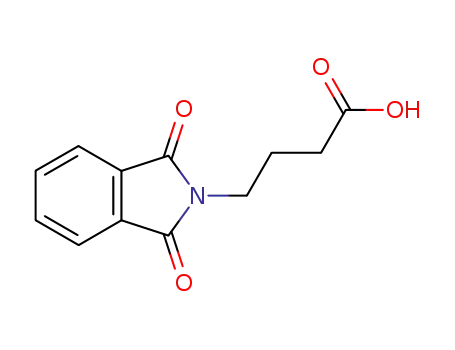
3130-75-4
4-phthalimidobutyric acid
-
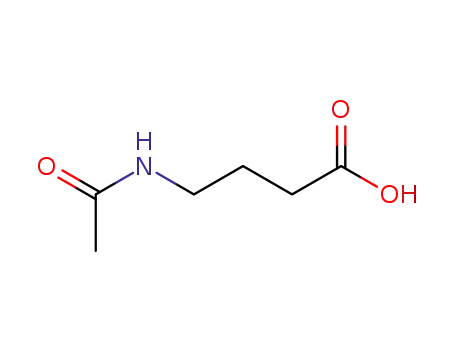
3025-96-5
N-Acetyl-4-aminobutyric acid
-
10466-75-8
4-(2,4-dinitro-anilino)-butyric acid
-
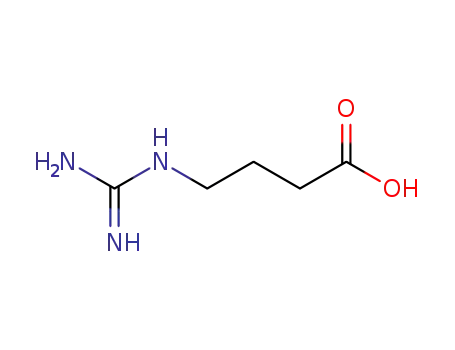
463-00-3
4-guanidinobutyric acid